Working Principle of Lithium Batteries
Working Principle of Lithium Batteries
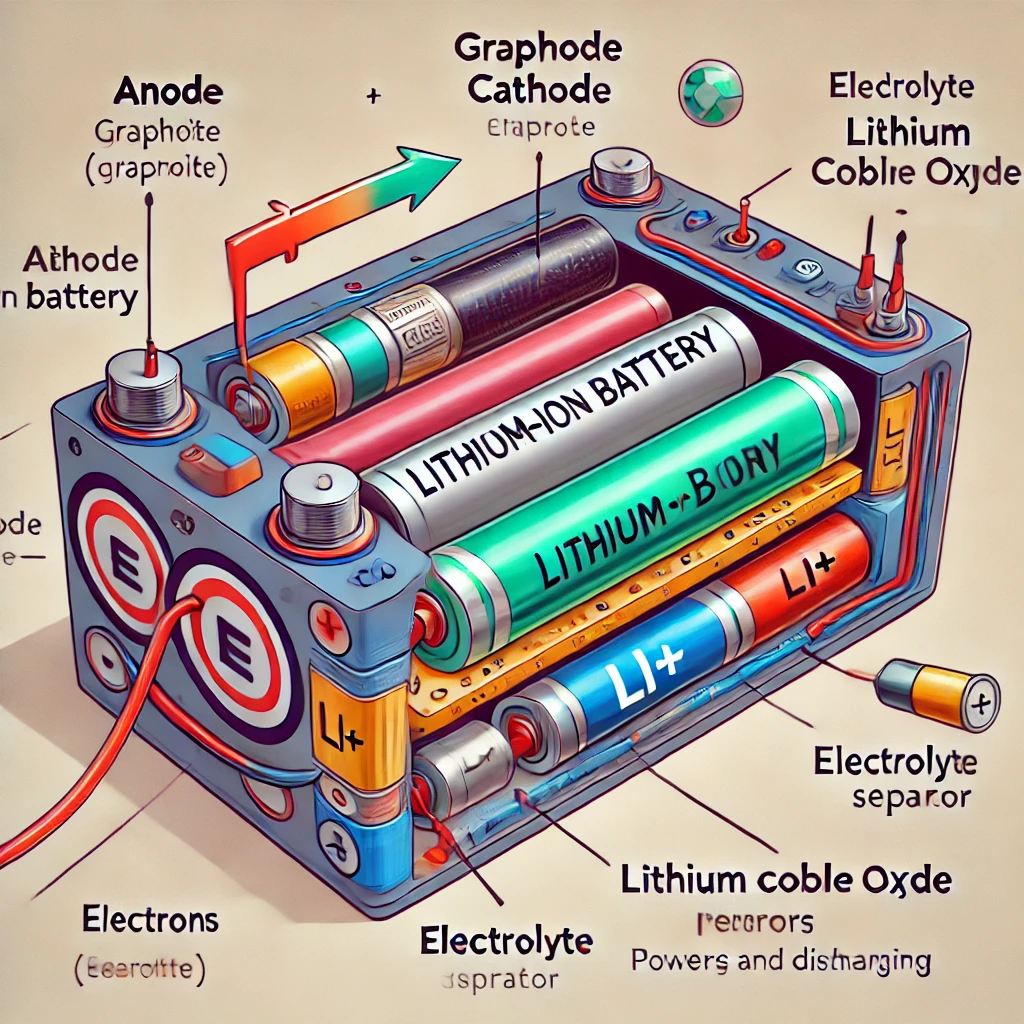
1. Basic Structure of a Lithium Battery
A lithium-ion (Li-ion) battery consists of four main components:
- Cathode: Usually made from lithium-containing compounds such as lithium cobalt oxide (LiCoO₂), lithium iron phosphate (LiFePO₄), or lithium nickel manganese cobalt oxide (NMC).
- Anode: Primarily made of graphite or silicon-carbon.
- Electrolyte: A lithium salt solution (LiPF₆) dissolved in an organic solvent.
- Separator: A porous material layer that separates the cathode and anode, allowing only lithium ions to pass through while preventing electrons from moving directly.
2. Working Principle of a Lithium Battery
Charging Process
- When charging, the external voltage pushes lithium ions from the cathode to the anode through the electrolyte.
- The lithium ions embed themselves in the graphite structure at the anode.
- Electrons move through the external circuit from the cathode to the anode to balance the charge.
Discharging Process
- During discharge (providing power), lithium ions leave the anode and travel through the electrolyte back to the cathode.
- Simultaneously, electrons move through the external circuit from the anode to the cathode, generating an electric current that powers devices.
3. Advantages of Lithium Batteries
- High energy density: Can store a lot of energy in a small size.
- Long lifespan: Can be charged and discharged multiple times without quickly degrading.
- High efficiency: Low energy loss, minimal memory effect compared to NiCd or NiMH batteries.
- Lightweight: Much lighter than lead-acid or NiMH batteries.
4. Disadvantages and Limitations
- Overheating risk: Overcharging or excessive discharging can lead to short circuits and potential fires/explosions.
- High cost: Manufacturing and material costs are more expensive than other battery types.
- Performance degradation over time: Energy storage capacity decreases after multiple charge cycles.
5. Applications of Lithium Batteries
- Smartphones, laptops, digital cameras (lightweight, high efficiency).
- Electric vehicles (EVs), e-bikes (lithium-ion and lithium iron phosphate batteries).
- Energy storage systems (solar power plants, backup batteries).
- Medical devices, aerospace industry (lithium-polymer batteries).
Lithium batteries are an advanced technology that provides efficient energy storage, but proper usage and maintenance are essential to ensure safety and longevity. 🚀