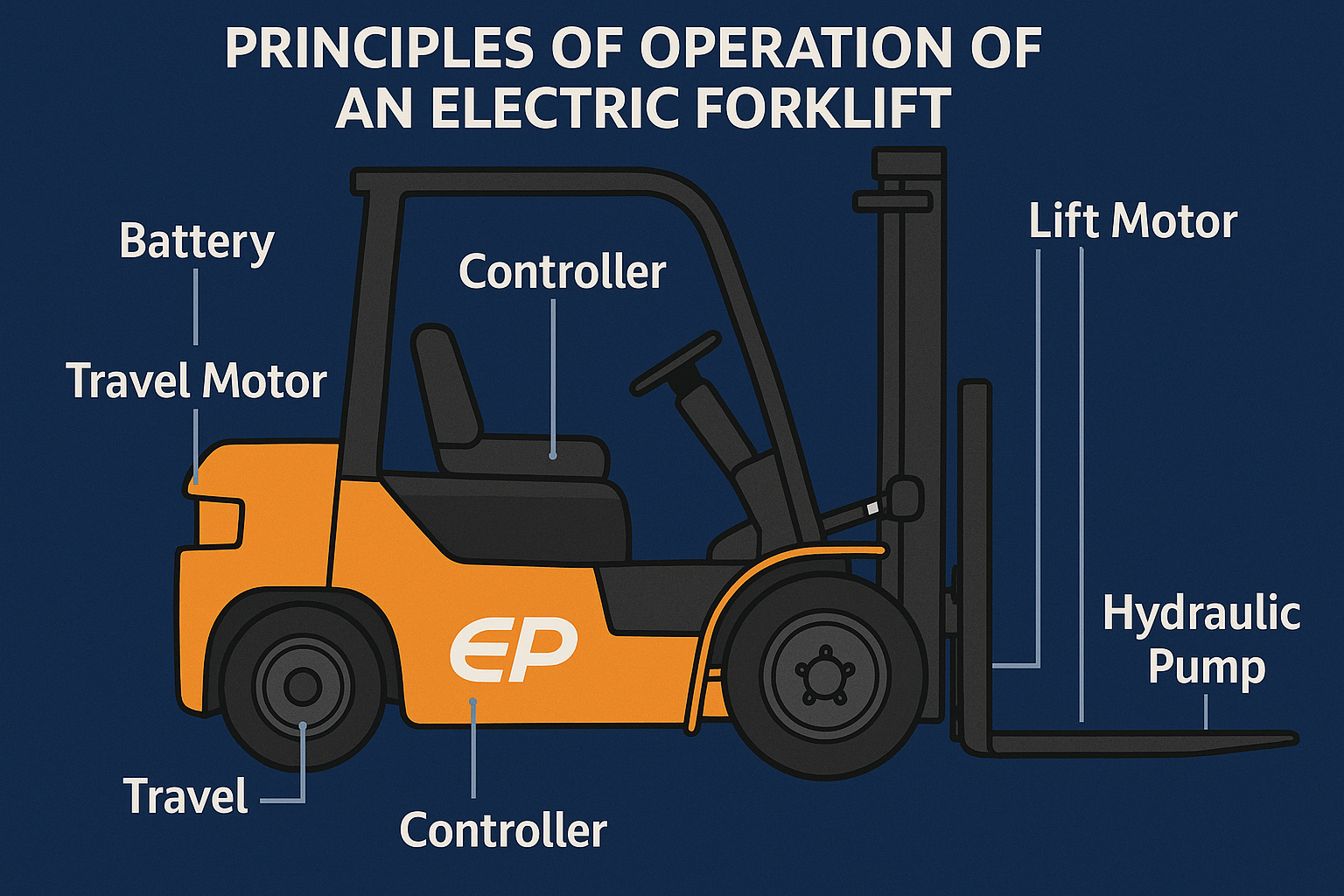
Working Principle of Electric Forklifts
The operation of electric forklifts is based on using an electric motor instead of an internal combustion engine like diesel or gasoline forklifts. The main working process is as follows:
1. Power Source
-
Uses batteries (lead-acid or lithium) as the power supply.
-
Common voltages: 24V, 48V, 80V depending on load capacity and design.
2. Control System (Controller)
-
The electronic controller adjusts the electric current supplied to the motor, allowing control over speed and lifting force.
-
Controlled via lever, throttle, or pedal.
3. Electric Motors
Electric forklifts usually have two types of motors:
-
Travel Motor: Drives the wheels for movement.
-
Lift Motor: Drives the hydraulic pump for lifting and lowering the forks.
4. Drive System
-
The electric motor transfers power through gears, belts, or directly to the wheels.
-
When the operator steps on the accelerator, the travel motor spins, causing the wheels to rotate.
5. Hydraulic Lifting System
-
When lifting or lowering, the lift motor activates the hydraulic pump.
-
The pump generates oil pressure, raising or lowering the piston cylinder and the forks.
6. Braking and Safety System
-
Uses electromagnetic or mechanical brakes.
-
Equipped with safety sensors, warning horns, and lights to assist the operator.
Summary of the Operation Principle:
Battery provides power → Controller regulates current → Motors run → Drive wheels & operate hydraulic pump → Move and lift.