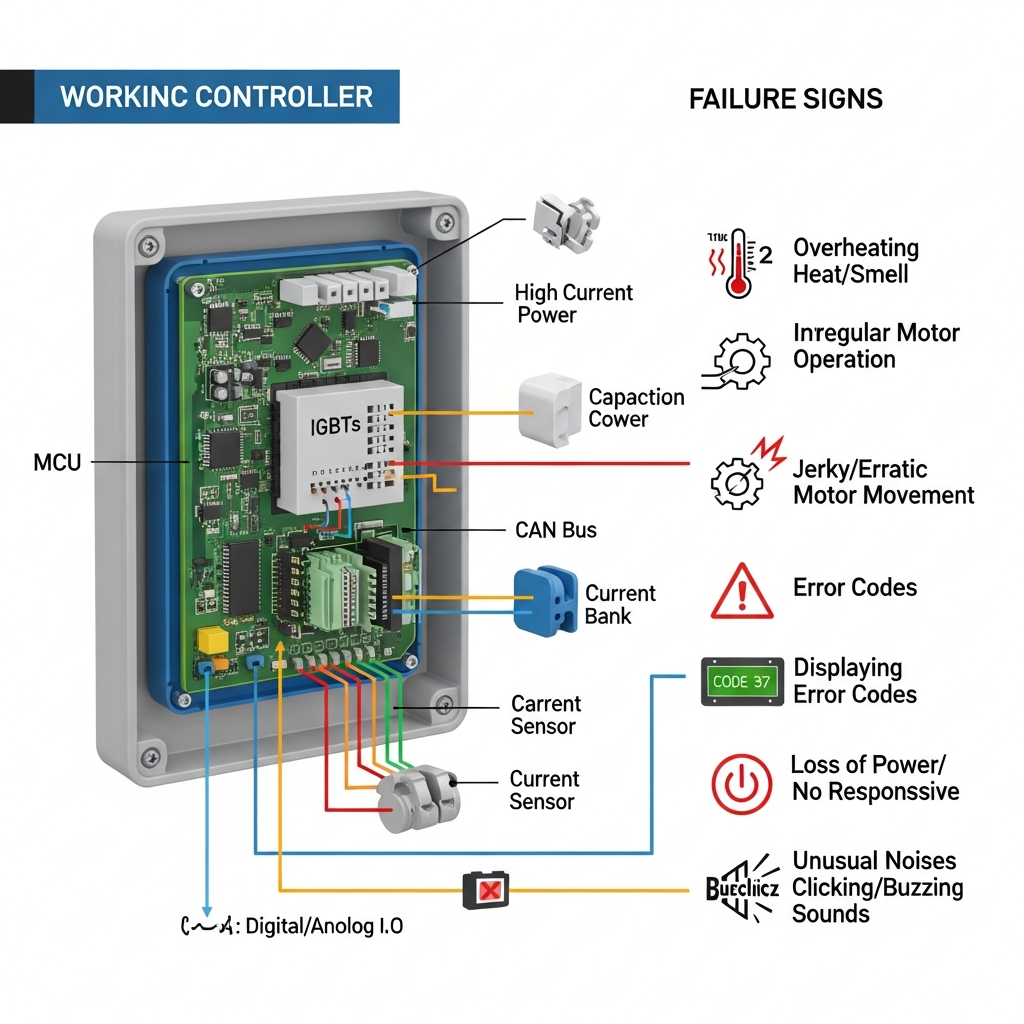
Structure of an Electric Forklift Controller – Working Principle & Failure Signs
What is an electric forklift controller?
An electric forklift controller is the central control unit of an electric forklift. It receives signals from the operator and sensors, processes them, and controls the driving and lifting motors safely and accurately.
👉 Simply put, the controller is the “brain” of an electric forklift.
Structure of an electric forklift controller
1️⃣ Power Input Section
-
Receives power directly from the battery: 24V / 36V / 48V / 80V
-
Includes:
-
B+ / B- terminals
-
Large power capacitors
-
Reverse polarity protection circuit
-
-
Function: stabilize voltage before supplying the controller
📌 Common failures: burnt capacitors, loose terminals → controller does not power on
2️⃣ DC-DC Converter (Low Voltage Power Supply)
-
Steps down high voltage to:
-
12V (relays, contactors)
-
5V / 3.3V (MCU, ICs)
-
-
Supplies power to the logic circuit
📌 DC-DC failure → controller completely dead
3️⃣ Main Microcontroller (MCU / CPU)
-
Commonly ARM-based or industrial-grade chips
-
Functions:
-
Process accelerator signals
-
Control driving, lifting, forward & reverse
-
Generate fault codes and manage safety logic
-
📌 Water damage often destroys MCU → difficult to repair
4️⃣ Power Module (IGBT / MOSFET)
-
The most critical part of the controller
-
Controls:
-
Motor speed
-
Driving torque
-
Direction of rotation
-
-
Operates via PWM (Pulse Width Modulation)
📌 Signs of IGBT failure:
-
Jerky movement
-
No driving despite having power
-
Repeated fuse blowing
5️⃣ Motor Drive Circuit
-
Includes:
-
IGBT driver circuits
-
Current shunt resistors
-
Current & temperature feedback circuits
-
-
Protects motor from overload and overheating
6️⃣ Signal Interface Section
Connected to:
-
Accelerator pedal (potentiometer / Hall sensor)
-
Forward / reverse switch
-
Lift / lower switch
-
Seat, brake, and safety switches
📌 Loose connectors may prevent the forklift from moving
7️⃣ Safety Protection Circuit
Protects against:
-
Overcurrent
-
Overtemperature
-
Low battery voltage
-
Short circuits
👉 When activated, the controller cuts motor output or displays a fault code.
8️⃣ Programming & Diagnostic Port
-
CAN / RS232 / RS485
-
Used for:
-
Parameter setting
-
Speed limitation
-
Fault diagnosis and clearing
-
Basic Working Principle
Signs of a faulty forklift controller
-
Forklift has power but does not move
-
Display does not turn on
-
Frequent fault codes
-
Weak or jerky operation
-
Fuses burn repeatedly
Maintenance & Repair Tips
✔️ Avoid high-pressure washing near the controller
✔️ Check wiring and connectors before replacing the controller
✔️ IGBT failures are often repairable
✔️ Long-term low battery voltage can damage the power section
❓ Frequently Asked Questions (Q&A)
Can a forklift controller be repaired?
👉 Yes. Power components such as IGBT, capacitors, or drivers can be repaired. MCU failure usually requires controller replacement.
Does “has power but won’t move” always mean controller failure?
👉 Not necessarily. It may be caused by a faulty accelerator, safety switch, or loose signal connector.
Is a faulty controller dangerous?
👉 Yes. It may cause brake failure, uncontrolled movement, or electrical damage.
When should the controller be replaced?
👉 When it is severely water-damaged, has multi-layer PCB damage, or the MCU cannot be reprogrammed.
Conclusion
Understanding the structure and working principle of an electric forklift controller helps technicians diagnose faults accurately and reduce unnecessary replacement costs.